https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00046-8
Regular Article
Bioconvection aspects in non-Newtonian three-dimensional Carreau nanofluid flow with Cattaneo–Christov model and activation energy
1
Department of Mathematics, Government College University Faisalabad, 38000, Faisalabad, Pakistan
2
College of Mathematics and Systems Science, Shandong University of Science and Technology, 266590, Qingdao, Shandong, China
Received:
8
August
2020
Accepted:
31
January
2021
Published online:
20
April
2021
In this article, a mathematical model is envisaged to scrutinize the aspect of swimming motile microorganisms for a steady 3D convectional flow of Carreau nanofluid towards a bidirectional stretching surface. Various researchers in the past years are collaborating in the nanotechnology field due to their improvement in heat capacity, chemotherapy for cancer, microelectronics, cooling of energy storage devices, cooling of nuclear system, air conditioning, and nanochips, etc. The novel concept of activation energy and double stratification effects is considered to analyze the flow problem. Thermal relaxation time and concentration relaxation time properties are both determined by implementing Cattaneo–Christov heat and mass flux in the energy and mass equation. Suitable similarity approximations are utilized to convert governing PDEs into dimensionless ODEs. Numerical solutions are determined to utilize collocation finite difference technique and 3-stages Lobatto-IIIa formula. The obtained ODE’s are resolved numerically by engaged built-in function bvp4c solver in computational software MATLAB. The behavior of various emerging parameters and local skin friction coefficients, local Nusselt numbers, local Sherwood number, motile microorganisms’ number, velocity profiles, temperature profile, concentration profile and microorganism concentration is elaborated with the help of graph and tables. Carreau fluid model is a particular category of established non-Newtonian fluid that exemplifies shear thinning 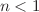 , shear thickening
, shear thickening 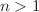 at high shearing rates. It is examined that the influence of the mixed convection parameter against temperature distribution both the temperature field of the shear-thinning/thickening liquids is reduced.
at high shearing rates. It is examined that the influence of the mixed convection parameter against temperature distribution both the temperature field of the shear-thinning/thickening liquids is reduced.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021




