https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-023-00881-x
Regular Article
New opportunities for kaonic atoms measurements from CdZnTe detectors
1
Dipartimento di Fisica e Chimica-Emilio Segrè, Università di Palermo, Viale Delle Scienze, Edificio 18, 90128, Palermo, Italy
2
Istituto Materiali per l’Elettronica e il Magnetismo, Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Parco Area delle Scienze 37/A, 43124, Parma, Italy
3
Stefan-Meyer-Institut für subatomare Physik, Kegelgasse 27, 1030, Vienna, Austria
4
Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, INFN, Via E. Fermi 54, 00044, Frascati, Italy
5
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, Bijenička cesta 32, 10000, Zagreb, Croatia
6
Horia Hulubei National Institute of Physics and Nuclear Engineering (IFIN-HH), No. 30, Reactorului Street, 077125, Magurele, Ilfov, Romania
7
Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria and INFN Sezione di Milano, Politecnico di Milano, Via Giuseppe Ponzio 34, 20133, Milano, Italy
8
Physik Department E62, Technische Universität München, James-Franck-Straße 1, 85748, Garching, Germany
9
Institute of Physical and Chemical Research, RIKEN, 2-1 Hirosawa, 351-0198, Wako, Saitama, Japan
10
Faculty of Physics, Astronomy, and Applied Computer Science, Jagiellonian University, ul. prof. Stanisława Łojasiewicza 11, 30-348, Kraków, Poland
11
Center for Theranostics, Jagiellonian University, ul. prof. Stanisława Łojasiewicza 11, 30-348, Kraków, Poland
12
Research Center for Electron Photon Science (ELPH), Tohoku University, 1-2-1 Mikamine, 982-0826, Taihaku-ku, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan
13
Centro Ricerche Enrico Fermi-Museo Storico della fisica e Centro Studi e Ricerche “Enrico Fermi”, Via Panisperna, 89a, 00184, Rome, Italy
14
Vienna Doctoral School in Physics, University of Vienna, Boltzmanngasse 5, 1090, Vienna, Austria
ax
alessandro.scordo@lnf.infn.it
Received:
13
September
2022
Accepted:
15
May
2023
Published online:
5
June
2023
We present the tests performed by the SIDDHARTA-2 collaboration at the 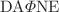 collider with a quasi-hemispherical CdZnTe detector. The very good room-temperature energy resolution and efficiency in a wide energy range show that this detector technology is ideal for studying radiative transitions in intermediate and heavy mass kaonic atoms. The CdZnTe detector was installed for the first time in an accelerator environment to perform tests on the background rejection capabilities, which were achieved by exploiting the SIDDHARTA-2 Luminosity Monitor. A spectrum with an
collider with a quasi-hemispherical CdZnTe detector. The very good room-temperature energy resolution and efficiency in a wide energy range show that this detector technology is ideal for studying radiative transitions in intermediate and heavy mass kaonic atoms. The CdZnTe detector was installed for the first time in an accelerator environment to perform tests on the background rejection capabilities, which were achieved by exploiting the SIDDHARTA-2 Luminosity Monitor. A spectrum with an 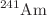 source has been acquired, with beams circulating in the main rings, and peak resolutions of 6% at 60 keV and of 2.2% at 511 keV have been achieved. The background suppression factor, which turned out to be of the order of
source has been acquired, with beams circulating in the main rings, and peak resolutions of 6% at 60 keV and of 2.2% at 511 keV have been achieved. The background suppression factor, which turned out to be of the order of  , opens the possibility to plan for future kaonic atom measurements with CdZnTe detectors.
, opens the possibility to plan for future kaonic atom measurements with CdZnTe detectors.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




