https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-023-00951-0
Regular Article
Time-reversal invariance violation and quantum chaos induced by magnetization in ferrite-loaded resonators
1
Lanzhou Center for Theoretical Physics and the Gansu Provincial Key Laboratory of Theoretical Physics, Lanzhou University, 730000, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
2
Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), 34126, Daejeon, Korea
Received:
21
April
2023
Accepted:
19
July
2023
Published online:
31
July
2023
We investigate the fluctuation properties in the eigenfrequency spectra of flat cylindrical microwave cavities that are homogeneously filled with magnetized ferrite. These studies are motivated by experiments in which only small pieces of ferrite were embedded in the cavity and magnetized with an external static magnetic field to induce partial time-reversal (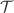 ) invariance violation. We use two different shapes of the cavity, one exhibiting an integrable wave dynamics, the other one a chaotic one. We demonstrate that in the frequency region where only transverse-magnetic modes exist, the magnetization of the ferrites has no effect on the wave dynamics and does not induce
) invariance violation. We use two different shapes of the cavity, one exhibiting an integrable wave dynamics, the other one a chaotic one. We demonstrate that in the frequency region where only transverse-magnetic modes exist, the magnetization of the ferrites has no effect on the wave dynamics and does not induce 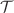 -invariance violation whereas it is fully violated above the cutoff frequency of the first transverse-electric mode. Above all, independently of the shape of the resonator, it induces a chaotic wave dynamics in that frequency range in the sense that for both resonator geometries the spectral properties coincide with those of quantum systems with a chaotic classical dynamics and same invariance properties under application of the generalized
-invariance violation whereas it is fully violated above the cutoff frequency of the first transverse-electric mode. Above all, independently of the shape of the resonator, it induces a chaotic wave dynamics in that frequency range in the sense that for both resonator geometries the spectral properties coincide with those of quantum systems with a chaotic classical dynamics and same invariance properties under application of the generalized 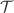 operator associated with the resonator geometry.
operator associated with the resonator geometry.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




