https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-024-01187-2
Review
Engineering of nanochannels in polymer membranes for energy and biological applications
1
Department of Physics, Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur, Jaipur, India
2
Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur, India
Received:
29
January
2024
Accepted:
23
May
2024
Published online:
4
June
2024
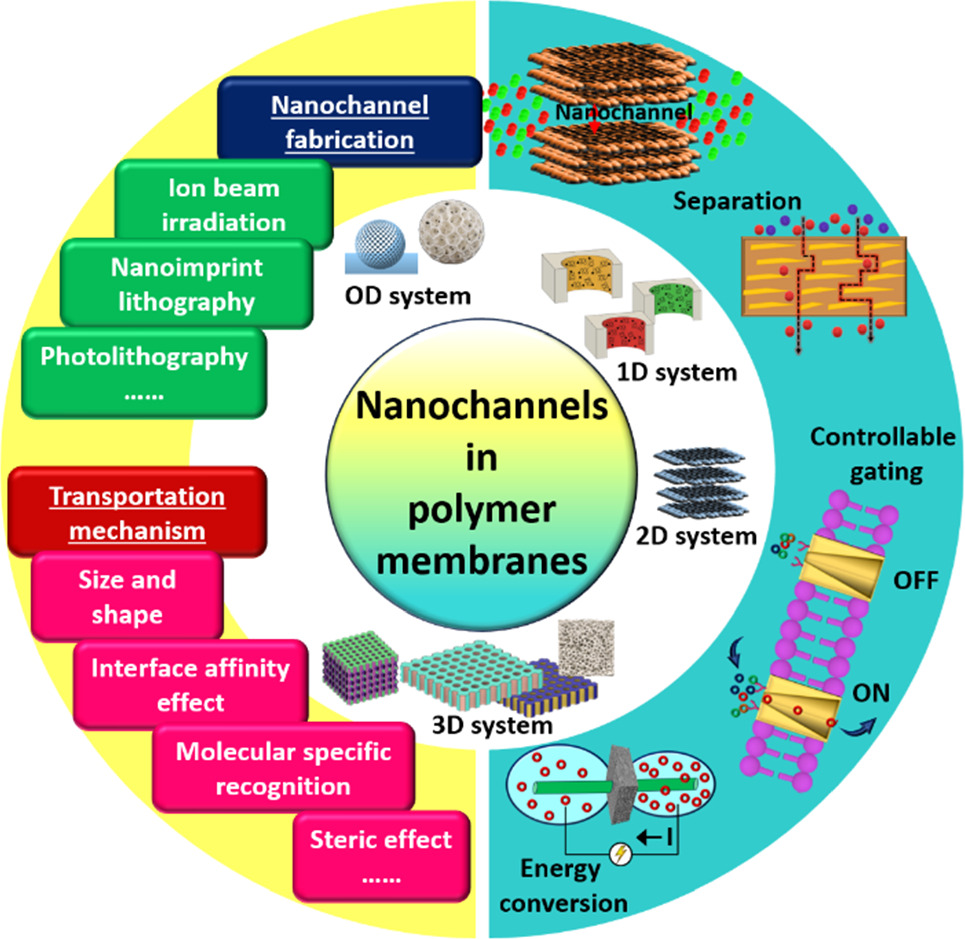
Nanochannels and their engineering within polymer membranes have emerged as a transformative way to address critical challenges in energy and biological applications. The multidisciplinary approach, through precisely controlling the nanoscale features to modify molecular transport and interactions, provides a range of innovative opportunities. In the realm of energy applications, these tailored nanochannels can enhance ion transport to benefit various energy storage and conversion devices, such as high-performance lithium-ion batteries and fuel cells, due to improved electrolyte management. In the biological domain, these engineered nanochannels with their selective transport of biomolecules provide the potential to revolutionize the treatment of diseases, and personalized medicine by precisely governing the passage of DNA, and proteins and offering unprecedented control in medical and biotechnological applications. The review explores the state-of-the-art techniques for engineered nanochannels within polymer membranes, with a focus on their fabrication methods and applications in various areas. It also discusses various advancements and innovative research going on to enhance the characteristics of nanochannels further. Moreover, it discusses the current challenges and future prospects in harnessing the nanochannels for sustainable energy solutions and advanced biological tools.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.