https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-024-01427-5
Regular Article
Scalp electroacupuncture reduces the oxidative stress in brain samples of chronically undernourished rats
1
Department of Acupuncture and Rehabilitation, State University of Ecatepec Valley, 55210, Ecatepec, Estado de México, Mexico
2
FES Iztacala, National Autonomous University of Mexico, 54090, Tlalnepantla, Estado de México, Mexico
3
Academic Area of Mathematics and Physics, Autonomous University of the State of Hidalgo, 42184, Mineral de la Reforma, Hidalgo, Mexico
4
Department of Physiology, Biophysics and Neuroscience, Center for Research and Advanced Studies, 07000, Mexico City, Mexico State, Mexico
Received:
31
May
2024
Accepted:
22
November
2024
Published online:
9
December
2024
This study was designed to evaluate the effect of scalp electroacupuncture (SEA) on the levels of hydroxyl radical (OH), malondialdehyde (MDA), and the catalase enzyme (CAT) in brain samples from chronically undernourished rats. Four groups of male Wistar rats (n=7 per group) were used: a) control group (C) that was given food ad libitum throughout the experimental period, b) chronically undernourished group (U), to which the food was reduced by half of the control food consumption from 3 weeks before mating, during mating, pregnancy and lactation, (c) chronically undernourished animals with scalp electroacupuncture treatment (U+SEA), and (d) chronically undernourished rats without EA stimulation (sham U-SEA). In U animals, the MDA (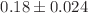 nmol MDA/
nmol MDA/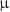 g protein,
g protein, 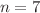 ) and ROH (
) and ROH (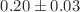 TBARS (
TBARS (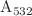 ),
), 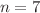 ) brain levels were significantly higher than those of the C group (
) brain levels were significantly higher than those of the C group (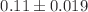 nmol MDA/
nmol MDA/ g protein;
g protein; 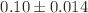 TBARS (
TBARS (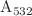 ), respectively;
), respectively; 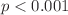 ). The levels of MDA (
). The levels of MDA (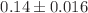 nmol MDA/
nmol MDA/ g protein;
g protein; 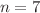 ) and ROH (
) and ROH (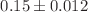 TBARS (
TBARS (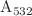 ),
), 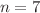 ) in the U-SEA group were lower than those of the C group, while no significant differences were observed in the sham U+SEA group. The antioxidant enzyme CAT showed significant differences between the C and the U group (
) in the U-SEA group were lower than those of the C group, while no significant differences were observed in the sham U+SEA group. The antioxidant enzyme CAT showed significant differences between the C and the U group (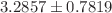 nmol
nmol 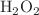 /
/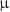 g of protein;
g of protein; 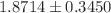 nmol
nmol 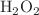 /
/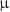 g of protein). After SEA, the CAT enzyme was increased (
g of protein). After SEA, the CAT enzyme was increased (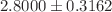 nmol
nmol 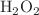 /
/ g of protein), but no significant difference was found in the sham U+SEA group. Our results suggest that chronically undernutrition increases the oxidative stress of the brain and SEA may exert a relevant antioxidative effect in the rat.
g of protein), but no significant difference was found in the sham U+SEA group. Our results suggest that chronically undernutrition increases the oxidative stress of the brain and SEA may exert a relevant antioxidative effect in the rat.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.





