https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-025-01532-z
Regular Article
Spatiotemporal dynamics in a network of modified Morris–Lecar neurons with nonlinear magnetic flux diffusion
1
Center for Nonlinear and Complex Networks, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, 600089, Chennai, India
2
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Vemu Institute of Technology, 517247, Chittoor, India
3
Department of Computer Science Engineering, PSCMR College of Engineering and Technology, 520001, Vijayawada, India
4
Center for Cognitive Science, Trichy SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Center, 621105, Trichy, India
5
Center for Research, Easwari Engineering College, Ramapuram, 600089, Chennai, India
Received:
26
December
2024
Accepted:
16
February
2025
Published online:
28
February
2025
In this work, a network of Morris–Lecar neurons with electromagnetic induction is imposed with nonlinear magnetic flux diffusion. We study wave propagation in a network of Morris–Lecar (ML) neurons with magnetic flux diffusion, connected to the local nodes of the nearest neighbors in a 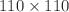 lattice of neurons with periodic boundary conditions. First, we explore the effect of various initial conditions on the modified ML neuron network without imposing external stimuli. Subsequently, we apply external stimuli at different positions and study wave propagation by changing the amplitude and frequency of the stimuli. The effects of varying Nernst potential of potassium ions, coupling strengths, and flux constants are also analyzed. The resulting collective dynamics of the considered neuronal network are provided in snapshots with different model parameters. This study offers a novel perspective on wave propagation in networks of biological neurons.
lattice of neurons with periodic boundary conditions. First, we explore the effect of various initial conditions on the modified ML neuron network without imposing external stimuli. Subsequently, we apply external stimuli at different positions and study wave propagation by changing the amplitude and frequency of the stimuli. The effects of varying Nernst potential of potassium ions, coupling strengths, and flux constants are also analyzed. The resulting collective dynamics of the considered neuronal network are provided in snapshots with different model parameters. This study offers a novel perspective on wave propagation in networks of biological neurons.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




