https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-025-01753-2
Regular Article
Effect of constant magnetic field on methemoglobinemia erythrocytes
1
Institute of Robotics “Saint Apostle and Gospeller Mathew”, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, (IR-BAS), P.O. Box 79, Acad. Georgi Bonchev, Bl. 2, 1113, Sofia, Bulgaria
2
Department of Genetics, Faculty of Biology, Sofia University “St. Kliment Ohridski”, 8 Dragan Tzankov Blvd., 1164, Sofia, Bulgaria
3
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Technical University of Sofia, 8 Kl. Ohridski Blvd., 1000, Sofia, Bulgaria
Received:
27
June
2024
Accepted:
16
June
2025
Published online:
8
July
2025
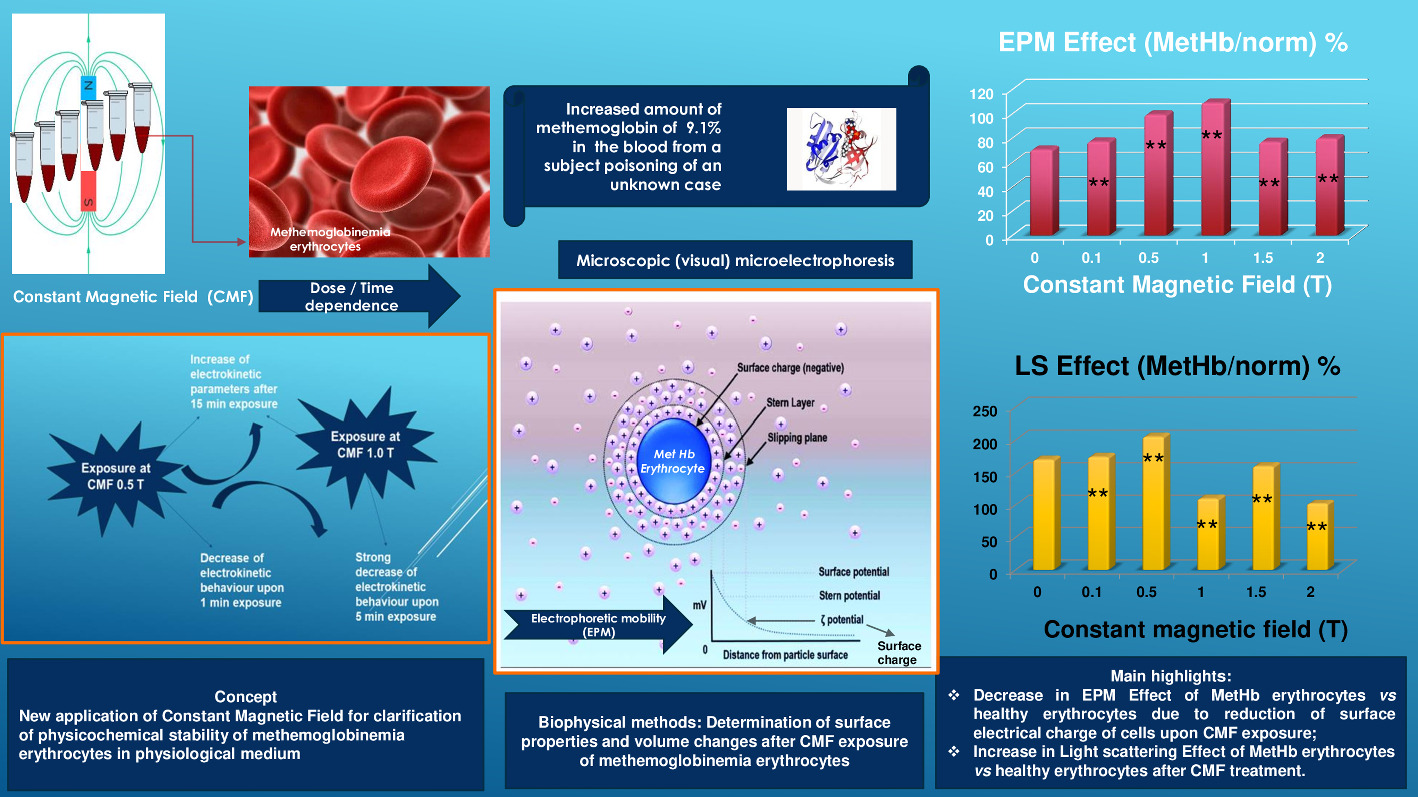
The effects of in vitro treatment of methemoglobinemia erythrocytes with constant magnetic field (CMF) are investigated which is certainly important from a biomedical point of view. The surface properties of the methemoglobinemia erythrocytes, which are characterized by an increased amount of methemoglobin of 9.1% in the blood is determined after exposition to in vitro influence CMF (0.1–2.0 T). Methemoglobinemia erythrocytes from a subject poisoning of an unknown case in phosphate buffered saline possess negative surface electrical charge at physiological medium. The treatment with CMF (0.1–2.0 T) increases the surface characteristics effect on methemoglobinemia cells versus this effect on healthy erythrocytes. This property is due to a strong increase in electrostatic repulsive forces between cells. The CMF altered significantly an increase in light scattering of the cells. Due to the increase of the negative electrokinetic potential under the influence of CMF from 0.5 to 1.0 T by approximately 3 mV, a time dependence of the effect of CMF on cells was found. Methemoglobinemia erythrocytes are exposed 1, 5, 10 and 15 min under the CMF electrical charge of cells at doses of 0.5 T (1 min), as well as at 1.0 T (5 min). The electrostatic free energy of erythrocytes is also calculated in order to determine the suitable thermodynamic reactions upon CMF exposure. Thus, a deeper understanding of the action of constant magnetic field on membrane level at methemoglobinemia erythrocytes is presented.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.