https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00039-7
Regular Article
Unsteady MHD flow of a Williamson nanofluid on a permeable stretching surface with radiation and chemical reaction effects
1
Department of Mathematics, SAS, VIT, 632014, Vellore, India
2
Department of Mathematics, University of Central Florida, 32816-1364, Orlando, FL, USA
b
laxminarayana.pallava@gmail.com
Received:
27
October
2020
Accepted:
31
January
2021
Published online:
12
April
2021
In the present work, we emphasize the impacts of an inclined magnetic field, viscous dissipation and radiation on the unsteady flow of a Williamson nanofluid over a vertical stretching porous surface with the presence of non-uniform heat source/sink and chemical reaction. In this study, we considered different kinds of nanoparticles such as silver, copper, aluminium oxide (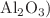 , titanium oxide (
, titanium oxide (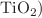 , and magnesium oxide (MgO). The basic equations of this investigation are transmuted into a system of nonlinear and coupled ODEs using suitable similarity variables and elucidated numerically by R.-K. Fehlberg-based shooting technique. Influences of the pertinent parameters on the velocity, the temperature and the concentration distributions are deliberated with the assistance of graphs and tables. This study depicts that
, and magnesium oxide (MgO). The basic equations of this investigation are transmuted into a system of nonlinear and coupled ODEs using suitable similarity variables and elucidated numerically by R.-K. Fehlberg-based shooting technique. Influences of the pertinent parameters on the velocity, the temperature and the concentration distributions are deliberated with the assistance of graphs and tables. This study depicts that 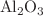 nanofluid has greater velocity since it has less dense nanoparticles compared to other nanoparticles. However, Cu-nanofluid has greater heat transfer due to greater thermal conductivity. Further, we identified that the thermal boundary layer thickness can be increased with the help of the viscous dissipation parameter. The inclination angle of the magnetic field strengthens the magnetic field on the fluid flow
nanofluid has greater velocity since it has less dense nanoparticles compared to other nanoparticles. However, Cu-nanofluid has greater heat transfer due to greater thermal conductivity. Further, we identified that the thermal boundary layer thickness can be increased with the help of the viscous dissipation parameter. The inclination angle of the magnetic field strengthens the magnetic field on the fluid flow
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021




