https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00058-4
Regular Article
Flow and heat transfer analysis of ethylene vinyl acetate nanofluid film in the process of tape casting
1
School of Science, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 100044, Beijing, China
2
Beijing Key Laboratory of Functional Materials for Building Structure and Environment Remediation, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 100044, Beijing, China
Received:
19
October
2020
Accepted:
5
February
2021
Published online:
6
May
2021
In industry, tape casting is an important way for the preparation of polymer thin films. Because the velocity and temperature controls in the casting process are related to the final quality of the film, this paper studies the flow and heat transfer behaviors of producing ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) nanofluid film by tape casting. Rheological experiment shows that the melted EVA (28% VA) is a power-law fluid. According to the similar principle of momentum transfer and energy transfer, the modified Fourier’s law is presented. And then, the corresponding new convective heat transfer equation has been established. Moreover, a power-law velocity slip model, which is well suited for describing the slip characteristics of polymer films, has been newly developed. With the skillful inverse variable transformation, the analytical solutions of velocity and temperature at any time and space are first presented. It is noteworthy that the heat transfer rate of power-law fluid is weaker than that of Newtonian fluid. Furthermore, it is observed that the temperature is reduced with the enhancement of both temperature control parameter d and the convective heat transfer coefficient 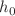 , which can ensure the best cooling effect.
, which can ensure the best cooling effect.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021




