https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-025-01603-1
Regular Article
Enhanced obesity classification with wavelet packet decomposition and ANN–PSO: a biomedical signal processing approach
1
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Zonguldak Bulent Ecevit University, 67100, Zonguldak, Turkey
2
Department of Computer Engineering, Turkish Naval Academy, National Defence University, 34942, Istanbul, Turkey
3
Department of Computer Engineering, Zonguldak Bulent Ecevit University, 67100, Zonguldak, Turkey
4
Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, University of Maribor, Koroška Cesta 160, 2000, Maribor, Slovenia
5
Community Healthcare Center Dr. Adolf Drolc Maribor, Vošnjakova ulica 2, 2000, Maribor, Slovenia
6
Complexity Science Hub Vienna, Josefstädterstraße 39, 1080, Vienna, Austria
7
Department of Physics, Kyung Hee University, 26 Kyungheedae-ro, Dongdaemun-gu, 02447, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Received:
18
February
2025
Accepted:
28
March
2025
Published online:
16
April
2025
Obesity diagnosis using biomedical signals has received increasing attention in recent years and requires advanced signal processing techniques in order to accurately classify obesity. In this context, this study proposes an intelligent diagnostic system for obesity classification using flash electroretinogram (fERG) signals, with a specific focus on cone responses. A novel feature extraction method based on Wavelet Packet Decomposition (WPD) is employed to decompose the cone responses into high- and low-frequency components, enabling detailed time–frequency analysis with high resolution. Subsequently, statistical features, such as mean, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis, are extracted from the decomposed signals and refined to enhance the training of artificial neural networks (ANNs). To optimize model performance, Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is integrated with ANN, resulting in an ANN–PSO hybrid model. The experimental dataset, comprising fERG signals from 47 subjects across diverse obesity categories, was utilized to evaluate the proposed hybrid model. The ANN–PSO model demonstrated high classification performance, achieving average accuracies of  and
and 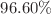 for right and left eye signals, respectively, outperforming traditional ANN models. These findings highlight the effectiveness of WPD in capturing intricate signal characteristics relevant to obesity levels and confirm the potential of the ANN–PSO model as a robust, efficient, and reliable diagnostic tool for clinical applications beyond conventional BMI assessments.
for right and left eye signals, respectively, outperforming traditional ANN models. These findings highlight the effectiveness of WPD in capturing intricate signal characteristics relevant to obesity levels and confirm the potential of the ANN–PSO model as a robust, efficient, and reliable diagnostic tool for clinical applications beyond conventional BMI assessments.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




