EPJ D Highlight - Investigating dense plasmas with positron waves
- Details
- Published on 19 February 2021
Astrophysical and lab-created plasmas under the influence of magnetic fields are the source of intense study. New research seeks to understand the dynamics of position waves travelling through these clouds of highly ionised gas.
The investigation of Electron-Positron-Ion (EPI) plasma — a fully ionised gas of electrons and positrons that includes astrophysical plasmas like solar winds — has attracted a great deal of attention over the last twenty years. A new study published in EPJ D by Garston Tiofack, Faculty of Sciences, University of Marousa, Cameroon, and colleagues, assesses the dynamics of positron acoustic waves (PAWS) in EPI plasmas whilst under the influence of magnetic fields, or magnetoplasmas.
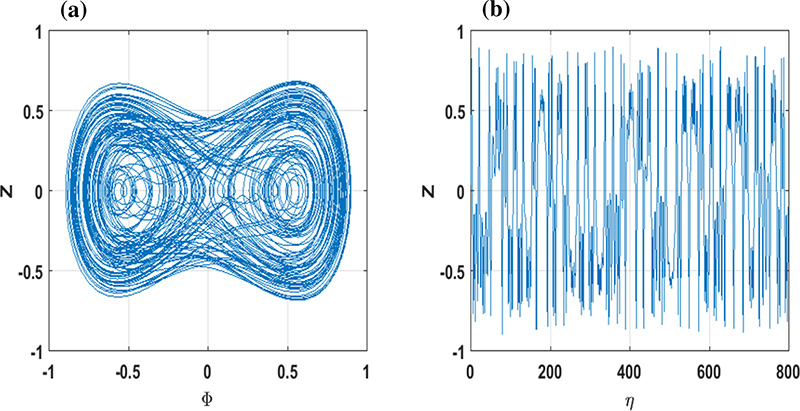
The authors studied the changes in PAWs using a framework of Korteweg-de Vries (KdV) and modified Korteweg-de Vries (mKdV) equations finding a former led to compressive positron acoustic solitary waves (PASWs), whilst the latter resulted in the same and additional rarefactive PASWs. Mathematical models and numerical simulations performed by the researchers also allowed them to consider the effect of various other factors on the magnetoplasma including the concentration of hot electrons to that of positrons and applied nonthermal parameters.
The team discovered that the transition to chaos in the magnetoplasma depends strongly on the frequency and strength of external periodic perturbations.
The study thus serves a useful guide to understanding the changes that occur at magnetoplasma in Auroral Acceleration Regions (AAR) and as they apply to PAWs. The team’s results could also help develop research into astrophysical plasma, which include solar flares and interstellar plasmas thus giving physicists a window into the processes that take place in extreme environments like active galactic nuclei and supernovae explosions.
Bringing the team’s research down to earth somewhat, it could also assist teams which generate plasma across the globe. These plasmas play a major role in a new generation of nuclear fusion reactors, which aim to generate clean power by replicating the processes that occur in the stars.
These plants use plasmas which are controlled with the use of powerful magnetic fields, thus making the understanding of such influences of critical importance to future clean energy production.
B.B. Mouhammadoul, C. G. L. Tiofack, A. Alim, A. Mohamadous (2021) Positron-acoustic travelling waves solutions and quasi-periodic route to chaos in magnetoplasmas featuring Cairns nonthermal distribution, European Physical Journal D 75:61, https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-020-00010-6




